General intelligence is referred to the existence of a mental capacity that influences the performance on cognitive level. The existence of general intelligence was proposed by Charles Spearman in 1904. General Intelligence is also known as g factor, but in simple terms, it can just be called intelligence.
The g factor is responsible for overall performance on mental ability tests. – Spearman
Spearman noted that while every individual excelled in certain areas, it wasn’t impossible for them to excel in other areas too. In fact, it was more common for an individual who specialized in certain areas to do well in other related areas. For instance, a person who excelled on verbal tests is highly likely to do well on other tests too.
This can also be related with athletes. There is no guarantee that a good footballer should be equally good in snowboarding. However, a good footballer is fit and athletic, so, he would have higher chances of performing physical tasks better than the individuals who are not as coordinated physically.
The basic idea is that the g factor, or general intelligence, influences performance on all cognitive tasks. The g factor can be measured by psychometric tests. The most accurate and profoundly used measure of intelligence is IQ tests.
The accumulation of cognitive testing data and improvements in analytical techniques have preserved gs central role and led to the modern conception of g.
Along with the introduction of general intelligence, Spearman also helped to develop a statistical technique called factor analysis. The method involves using varieties of test items in order to measure common abilities. For instance, a person who does well on reading comprehension tests will also perform better in verbal tests.
General intelligence represented an intelligence factor underlying specific mental abilities. – Spearman
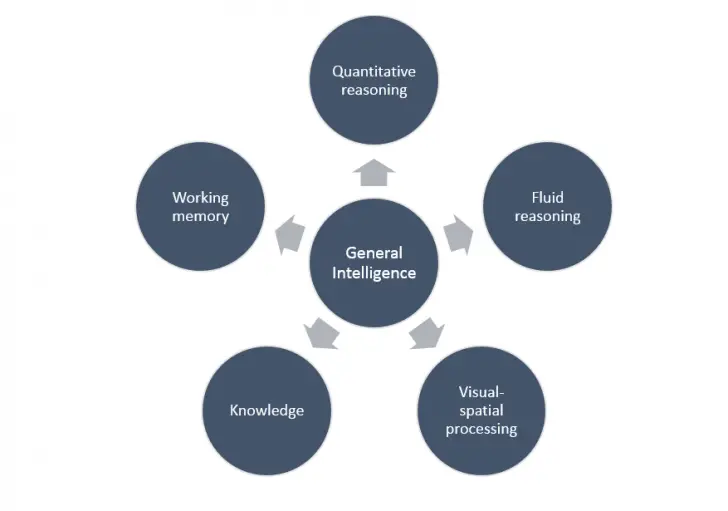
Meaning, all tasks compiled in intelligent tests are influenced by the general intelligence of the person. Modern intelligence tests like Stanford-Binet are thought to measure various cognitive factors that make up general intelligence. The tests include
- quantitative reasoning:
the test that involves capacity to solve numerical problems - fluid reasoning :
flexible thinking to solve problems - visual-spatial processing:
ability to put together puzzles and copying complex shapes - knowledge:
a person’s knowledge about vast array of topics - working memory:
capacity of the short term memory, such as repeating a list
Critical Evaluation
The idea of measuring intelligence with a single number based on an IQ test has remained controversial till date. The concept of g factor has been ridiculed by carious psychologists because of it.
Howard Gardner, a renowned psychologist, proposed a theory of multiple intelligences as opposed to the Spearman’s General Intelligence theory. Gardner’s intelligences consisted of abilities in various domains such as logical-mathematical intelligence, spatial intelligence, and so on.
Because general intelligence is the underlying ability that determines performance on wide range of cognitive tasks, IQ scores are often considered a predictive factor of individual’s success in life. However, even if a person manages to maintain academic success and good career, overall success isn’t simply limited to these factors. Other factors like motivation, socio-economic status, personality, maturity, childhood experiences, are also vital in determining one’s overall success.