The reinforcers which are biologically important are called Primary Reinforcers. It is also referred as unconditional reinforcement. These reinforcers occur naturally without having to make any effort and do not require any form of learning. For example: food, sleep, water, air and sex.
Primary reinforcements are naturally occurring and do not require an individual to learn any significant method or process in order to work. Most primary reinforcers are backed by an evolutionary basis. They have been occurring since the beginning of time and aid the survival of the species.
Even though primary reinforcers are natural, factors like experience and genetics also play a role in reinforcing such things.
For instance, a person might prefer a certain type of food extra rewarding, while the choice might be completely different for another individual.
Examples
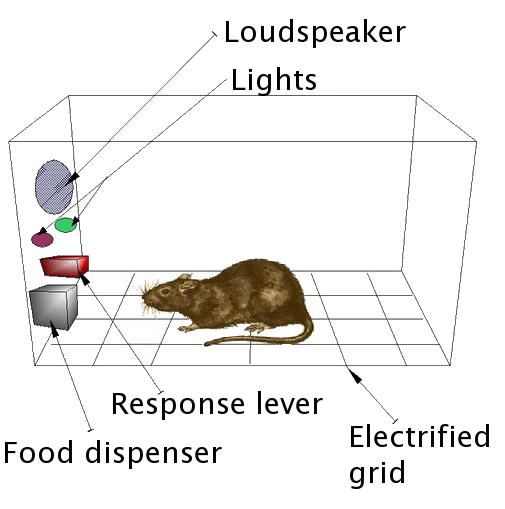
Example 1: The rat in the Skinner box rewarded with food when it managed to press the lever.
Example 2: Taking a pill for the headache to go away.
It has been seen that primary reinforcers are more effective than secondary reinforcers (conditioned reinforcers) when it comes to results. A hungry child is more likely to finish his homework in time if he is promised to be offered food, rather than a child doing assignments for good grades.
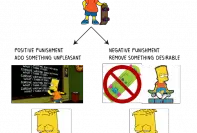
Also, primary reinforcers are used for both Positive Reinforcement and Negative Reinforcement.